
PKCS#11

| Cryptographic Token Interface Standard |
PKCS#11 |
Sections | |
| X.509 attribute certificate objects | |
The following figure illustrates details of certificate objects:
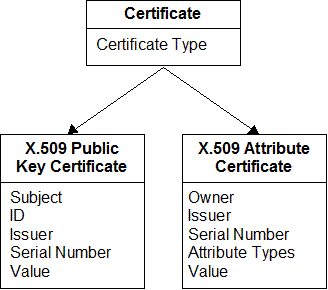
Certificate objects (object class CKO_CERTIFICATE) hold public-key or attribute certificates. Other than providing access to certificate objects, Cryptoki does not attach any special meaning to certificates. The following table defines the common certificate object attributes, in addition to the common attributes listed in Table 15 and Table 19 :
Table 21, Common Certificate Object Attributes
| Attribute | Data type | Meaning |
| CKA_CERTIFICATE_TYPE1 | CK_CERTIFICATE_TYPE | Type of certificate |
| CKA_TRUSTED | CK_BBOOL | The certificate can be trusted for the application that it was created. |
1Must be specified when the object is created.The CKA_CERTIFICATE_TYPE attribute may not be modified after an object is created.
The CKA_TRUSTED attribute cannot be set to TRUE by an application. It must be set by a token initialization application. Trusted certificates cannot be modified. X.509 public key certificate objects
X.509 certificate objects (certificate type CKC_X_509) hold X.509 public key certificates. The following table defines the X.509 certificate object attributes, in addition to the common attributes listed in Table 15 , Table 19 and Table 21 :
Table 22, X.509 Certificate Object Attributes
| Attribute | Data type | Meaning |
| CKA_SUBJECT1 | Byte array | DER-encoding of the certificate subject name |
| CKA_ID | Byte array | Key identifier for public/private key pair (default empty) |
| CKA_ISSUER | Byte array | DER-encoding of the certificate issuer name (default empty) |
| CKA_SERIAL_NUMBER | Byte array | DER-encoding of the certificate serial number (default empty) |
| CKA_VALUE1 | Byte array | BER-encoding of the certificate |
1Must be specified when the object is created.
Only the CKA_ID, CKA_ISSUER, and CKA_SERIAL_NUMBER attributes may be modified after the object is created.
The CKA_ID attribute is intended as a means of distinguishing multiple public-key/private-key pairs held by the same subject (whether stored in the same token or not). (Since the keys are distinguished by subject name as well as identifier, it is possible that keys for different subjects may have the same CKA_ID value without introducing any ambiguity.)
It is intended in the interests of interoperability that the subject name and key identifier for a certificate will be the same as those for the corresponding public and private keys (though it is not required that all be stored in the same token). However, Cryptoki does not enforce this association, or even the uniqueness of the key identifier for a given subject; in particular, an application may leave the key identifier empty.
The CKA_ISSUER and CKA_SERIAL_NUMBER attributes are for compatibility with PKCS #7 and Privacy Enhanced Mail (RFC1421). Note that with the version 3 extensions to X.509 certificates, the key identifier may be carried in the certificate. It is intended that the CKA_ID value be identical to the key identifier in such a certificate extension, although this will not be enforced by Cryptoki.
The following is a sample template for creating a certificate object:
CK_OBJECT_CLASS class = CKO_CERTIFICATE; CK_CERTIFICATE_TYPE certType = CKC_X_509; CK_UTF8CHAR label[] = "A certificate object"; CK_BYTE subject[] = {...}; CK_BYTE id[] = {123}; CK_BYTE certificate[] = {...}; CK_BBOOL true = TRUE; CK_ATTRIBUTE template[] = { {CKA_CLASS, &class, sizeof(class)}, {CKA_CERTIFICATE_TYPE, &certType, sizeof(certType)}; {CKA_TOKEN, &true, sizeof(true)}, {CKA_LABEL, label, sizeof(label)-1}, {CKA_SUBJECT, subject, sizeof(subject)}, {CKA_ID, id, sizeof(id)}, {CKA_VALUE, certificate, sizeof(certificate)} };